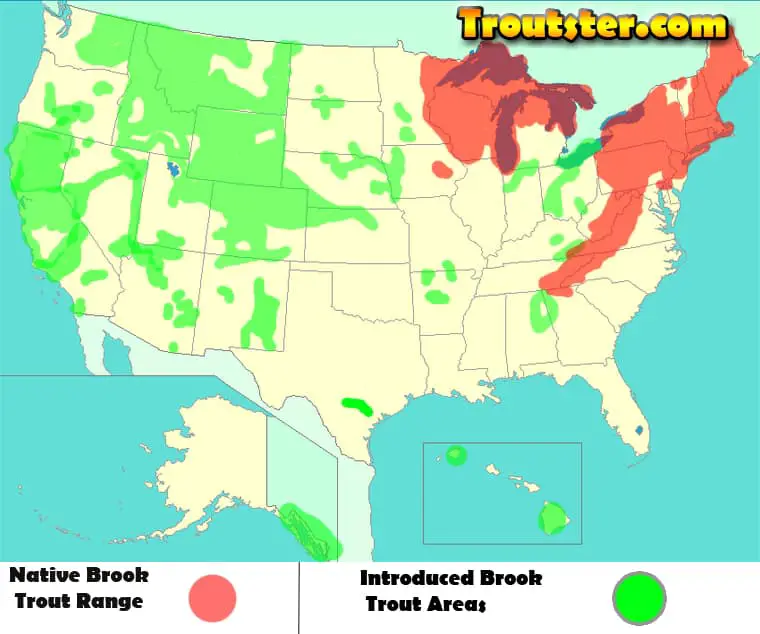
Brook Trout Introduction Into Non Native Areas
Brook trout are a common and sought after sport fish (especially fly fisherman), because of this, they are planted regularly in many areas. Brook trout have been planted in several countries such as: Argentina, Australia, Austria, Belgium, Bolivia, Bulgaria, Canada, Chile, Colombia, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, India, Iran, Italy, Japan, Kenya, Latvia, Lithuania, Mexico, Morocco, Netherlands, New Zealand, Norway, Papua New Guinea, Peru, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Russian Federation, Serbia and Montenegro, Slovakia, Slovenia, South Africa, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Turkey, United Kingdom, Venezuela, Zimbabwe. (Source)
Negative Effects of Planting of this Species
In areas where brook trout have been planted, it is common for them to do damage to (if not exterminate) other species of animals. Despite the small size of these fish, they are actually very aggressive. They have caused significant damage to many species of frogs, not to mention the terrible damage to other species of fish.
Interbreeding and Aggressive Nature
The brook trout has been known to breed with bull trout, which is considered a species of concern in many areas. Since the brook and bull trout are close relatives, they can successfully breed with each other, however their offspring are sterile. This hybridization between these 2 species has had very detrimental effects to the bull trout populations where the brook trout has been introduced.
Brook trout are also known to compete heavily with the native cutthroat in some western States. In many cases this species has managed to completely replace entire populations of cutthroat trout such as the greenback cutthroat in some of it’s native waters in Colorado. “In Black Hollow Creek, near Fort Collins, Colorado, stocked brook trout completely replaced greenback cutthroat trout O. clarki stomias within a period of five years (Behnke 1992, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service 1995).” (source)
